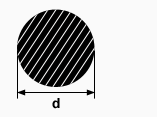
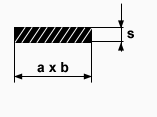
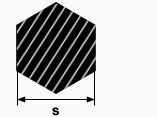
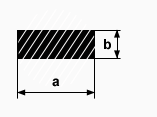
Informations about the offered assortment
Supplied assortment
1.3952, 1.4910, 1.4429 – High-alloy steel
100Cr6, 1.3505, 1.2067, A295, 14109, 14100, SHKH15 – Bearing steel
10CrMo9-10, 1.7380, 15313, 10KH2M – heat resistant steel
13CrMo4-5, 1.7335, 15121, 12KHM, 15KHM – High temperature steel
14MoV6-3, 1.7715, 12Kh1MF – High temperature steel
15NiCr13, 1.5752, 16420 – Alloy steel
16Mo3, 1.5415 – High temperature steel
17CrNi6-6, 1.5918, 15CrNi6, 1.5919, 16220 – Engineering Steel
21CrMoV5-7, 1.7709, 15236 – High temperature steel
24CrMoV5-5, 1.7733, ~15320 – Construction steel
25CrMo4, 1.7218, 15130 – Engineering steel
30CrNiMo8, 1.6580, 16430 – Structural steel
31CrMoV9, 30CrMoV9, 1.7707, 1.8519, 15330 – Nitriding steel
34CrAlNi7-10, 1.8550 – Nitriding steel
34CrNiMo6, 1.6582, 16343 – Construction steel
37MnSi5, 1.5122, 13240 – Construction steel
40CrMoV4-6, 1.7711, ASTM A 193 B16 – Construction steel
51CrV4, 50CrV4, 1.8159, ~15260 – Spring steel
C35,C35E, C35R, 1.0501, 1.1180, 1.1181, 12040 – Carbon steel
P250GH, P245GH, A105, 1.0460, C22.8, 12024 – Boiler steel
P265GH, 1.0425 – Carbon Steel
P355NL1, P355NL2, P355NH, P355GH, 1.0565, 1.0566, 1.0473 – mild, structural steel
X10CrMoVNb9-1, 1.4903 – Heat-resistant stainless steel boiler
X10CrNiMoTi18-10, 1.4571, 17348 – Stainless steel
X12Cr13, 1.4006, 17021 – Stainless steel
X19CrMoNbVN11-1, 1.4913 – High temperature stainless steel
X20Cr13, 1.4021, 1.4022 – Stainless steel
X22CrMoV12-1, 1.4923, 17134 – High temperature stainless steel
X6CrNiTi18-10, 1.4541, 17248 – Stainless steel
Steel weight calculation